Gauss Theorem Egregium - If a curved surface is developed upon any other surface. 4 Theorema Egregium The following theorem represents one of the most important theorems within the eld of di erential geometry and the study of surfaces.
The Curvature Tensor and the Theorema Egregium 1 18 The Curvature Tensor and the Theorema Egregium Recall.
Gauss theorem egregium. Gausss view of curvature and the Theorema Egregium Differential Geometry 35 NJ. One of Gausss most important discoveries about surfaces is that the gaussian curvature is unchanged when the surface is bent without stretching. Gausss Theorema Egregium.
The Gauss curvature of a surface in R3 depends on EFGand their derivatives only in a local parametrization. Curves on a surface. This is a preview of subscription content log in to check access.
We can show that the standard sphere in R3 is not locally isometric to the plane. Thus the Theorema Egregium takes the form Theorem. Once he realized that he then set out to do the computation in Theorema Egregium and of course he succeeded in carrying it out.
According to Spivak Gauss showed that the Gaussian curvature is intrinsic by taking the limit using the now called Gauss-Bonnet Theorem for geodesic triangles. Local Isometries First Fundamental Form Gaussian Curvature Gauss Equations These yield Gauss Theorema Egregium Also known as Gauss Remarkable Theorem By Cheyenne Trimmer and Kristin Hill. Chapter 4 on the Theorema Egregium deals with the main contributions by Gauss as developped in his Disquisitiones generalis circa superficies curvas General investigations on curved surfaces from 1827.
Also it allows you to define what is the angle between two tangent vectors. The Gauss curvature is intrinsic. Let M be a regular surface.
We shall deduce the Theorema Egregium from two results which relate the first and second fundamental forms of a surface and. Theorema Egregium t ou Gauss MÐa apì ti c shmantikì terec anakalÔyei t ou Gauss perÐ epifanein eÐ nai o ì h kampulì tht a Gauss paramènei analloÐwth ì t an h epif neia k mptet ai qwrÐ c na tentnet ai. If n 2 then the only nontrivial component of the Riemann curvature tensor is K Re 1e 2e 1e 2 H 11H 22 H 2 12.
Theorema Egregium1 If f. We have shown Theorem I-5 that the Gauss curvature at a point P is KP Lg where L is the Second Fundamental Form and g is. If p in M C_epsilon and D_epsilon are the polar circle and polar disk.
And the equations 11 are the Gauss equations. If gis the metric induced on Uby the Gauss curvature of gis given by K pg det P LN M2 EG F2. Spontaneously leads to excellent the following Theorem.
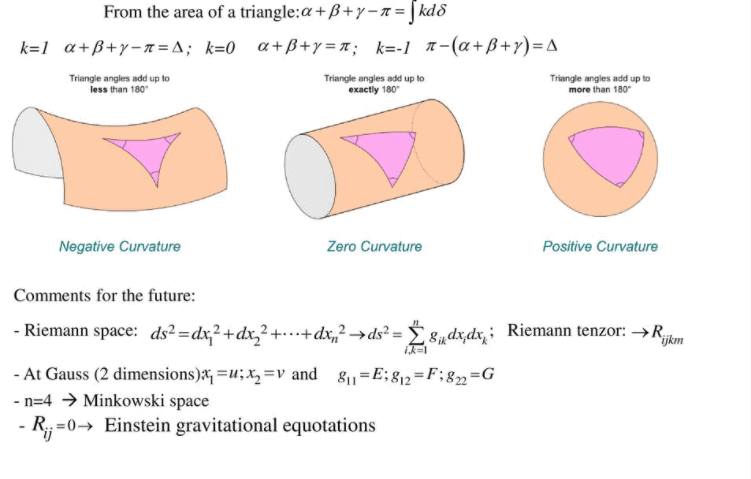
Remarkable theorem states that Gaussian curvature of a surface can be determined from the measurements of length on the surface itself. The theorem states that The Gaussian curvature of a surface does not change if one bends the surface without stretching it. Theorema Egregium Remarkable Theorem Gauss Theorema Egregium is a result of differential geometry that talks about the curvature of surfaces.
Gauss Theorema Egregium Foundational result in differential geometry that concerns the curvature of surfaces Proved by Carl Friedrich Gauss Recall. In fact it can be found given the full knowledge of the first fundamental form and expressed via the first fundamental form and its partial derivatives of first and second order. The Gaussian probability distribution is named after Gauss.
This theorem states that the Gaussian curvature is unchanged when the surface is bent without stretching. Gausss theorema egregium states that the Gaussian curvature of a surface embedded in three-space may be understood intrinsically to that surface. In 1828 he published his Disquisitiones generales circa superficies curvas or General investigation of curved surfaces.
Theorema Egregium tells you that all this information suffices to determine the Gaussian Curvature. A map preserving the Gauss curvature is not necessarily a local isometry see Remark 1011. The Theorema Egregium Remarkable Theorem is an important theorem of Carl Friedrich Gauss concerning the curvature of surfaces.
Gauss called it Theorema Egregium meaning remarkable theorem since it. The converse is false. Made important contributions to statistics and probability theory.
O Gauss o nìmase autì apo tèlesma egregium kai h lati nik lèxh gia t o exèqo n paramènei apì tì te. Theorem 101 Theorema Egregium. Informally the theorem says that the curvature of a surface can be determined entirely by measuring angles and distances on the surface that is it does not depend on how the surface might be embedded in 3-dimensional space.
Si superficies curva in quamcumque aliam superficiem explicatur mensura curvaturae in singulis punctis invariata manet. One of greatest achievements of Carl Friedrich Gauss was a theorem so startling that he gave it the name Theorema Egregium or outstanding theorem. This chapter is a highlight of these lectures and altogether we shall discuss four different proofs of the Theorema Egregium.
The most important theorem here is the famous Theorema Egregium which says that the Gauss curvature Kde ned previously using the shape operator S which is an extrinsic object is indeed an intrinsic curvature which can be computed from the rst fundamental form gand its derivatives only. Gausss Theorema egregium Latin. Gauss called this result egregium and the Latin word for remarkable has remained attached to his theorem ever since.
S 1 S2 is a local isometry then the Gauss curvature of S1 at P equals the Gauss curvature of S2 at fP. Gausss view of curvature and the Theorema Egregium Differential Geometry 35 NJ Wildberger - YouTube. Gauss called this result egregium and the Latin word for remarkable has remained attached to his theorem ever since.
A property of a surface which depends only on the metric form is an intrinsic property. Which is known as the Gauss curvature and equation 10 is the Theorem Egregium of Gauss. The theorem can only be used to rule out local isometries between surfaces.
A local isometry preserves the Gauss curvature. Residents of the surface may observe the Gaussian curvature of the surface without ever venturing into full three-dimensional space. Gauss theorem can be stated as follows.
Gauss defined a quantity that measures the curvature of a two-dimensional surface. Share Improve this answer answered Apr 20 12 at 2204. They can observe the curvature of the.
In his Disquisitiones generales circa superficies curvas 1827 12 page 24 Gauss called egregium sponte perducit ad egregium ie. For example using the following. Proved the Theorema Egregium a major theorem in the differential geometry of curved surfaces.

Gauss Theorema Egregium Springerprofessional De

Theorema Egregium Simple English Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia
Gauss Theorema Egregium By K Hill

Theorema Egregium Youtube

How A 19th Century Math Genius Taught Us The Best Way To Hold A Pizza Slice Part 1 Mathnasium

Gauss S View Of Curvature And The Theorema Egregium Differential Geometry 35 Nj Wildberger Youtube

Theoremoftheday Auf Twitter Today S Theorem Gauss S Theorema Egregium Attention Flat Earthers An Oblate Spheroid Does Not Have Zero Gaussian Curvature Https T Co Dxdtdmniao
Uregina Ca

Cylinder Bucket Theorema Egregium Mathematics Bucket Bucket Theorema Egregium Png Pngegg
Theoremoftheday Org

The Fun Side Of Mathematics Theorema Egregium By Ekaterina Semyanovskaya The Fun Side Of Mathematics Theorema Egregium Medium
13 Gauss S Theorema Egregium

Gaussian Curvature Wikiwand

Forget About Pornstars Upvote Gauss S Theorema Egregium Imgur